иҮӘдё»жңәеҷЁдәә
- йҮҚеһӢиҪҰиҫҶ
- жұҪиҪҰ
- и®ҫеӨҮдёҺжңәжў°
- зҰ»ж•ЈеҲ¶йҖ
жіўеЈ«йЎҝе’ЁиҜўйӣҶеӣўдҝқе®Ҳең°йў„жөӢпјҢеҲ° 2025 е№ҙпјҢиҜҘеёӮеңәе°ҶиҫҫеҲ° 870 дәҝзҫҺе…ғгҖӮ
иө„ж–ҷжқҘжәҗпјҡжңәеҷЁдәәжҠҘе‘Ҡ
з”өж°”е·ҘзЁӢе…¬еҸёиҘҝй—Ёеӯҗйў„жөӢпјҢе…ЁзҗғиҮӘеҠЁжңәеҷЁдәәеёӮеңәе°ҶеңЁ 2019 е№ҙеўһй•ҝеҲ° 36 дәҝзҫҺе…ғпјҢеҲ° 2023 е№ҙе°Ҷеўһй•ҝеҲ° 139 дәҝзҫҺе…ғгҖӮ
иө„ж–ҷжқҘжәҗпјҡ иҘҝй—Ёеӯҗ
2016 е№ҙе…ЁзҗғиҮӘдё»жңәеҷЁдәәеёӮеңәд»·еҖјзәҰдёә 46 дәҝзҫҺе…ғпјҢйў„и®ЎеҲ° 2024 е№ҙе°Ҷи¶…иҝҮ 119 дәҝзҫҺе…ғгҖӮйў„и®Ў 2017 е№ҙиҮі 2024 е№ҙжңҹй—ҙзҡ„еӨҚеҗҲе№ҙеўһй•ҝзҺҮе°Ҷи¶…иҝҮ 14%гҖӮ
иө„ж–ҷжқҘжәҗпјҡ е…Ёзҗғж–°й—»дё“зәҝ
иҮӘдё»жңәеҷЁдәәдҪ•ж—¶е®һз”Ёпјҹ
еҪ“ж»Ўи¶ід»ҘдёӢдёӨдёӘж ҮеҮҶд№ӢдёҖж—¶пјҢиҮӘдё»жңәеҷЁдәәзү№еҲ«жңүз”Ёпјҡ
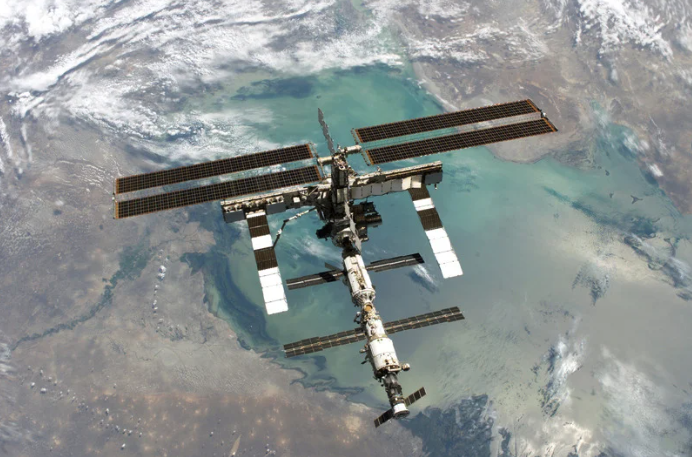
1. зҺҜеўғеҜ№дәәзұ»жқҘиҜҙиҰҒд№ҲжҳҜеҚұйҷ©зҡ„пјҢиҰҒд№ҲжҳҜжҳӮиҙөзҡ„гҖӮдҫӢеҰӮпјҢиҲӘеӨ©е’Ңжү«йӣ·йғҪжҳҜдәәзұ»жҙ»еҠЁзҡ„еҚұйҷ©йўҶеҹҹгҖӮз”ұдәҺеңЁеӨӘз©әдёӯж”ҜжҢҒдәәзұ»з”ҹжҙ»зҡ„жҲҗжң¬пјҢеӨӘз©әйЈһиЎҢд№ҹйқһеёёжҳӮиҙөгҖӮ
2. иҜҘд»»еҠЎйңҖиҰҒз®ҖеҚ•гҖҒ常规зҡ„еӨ§йҮҸеҠЁдҪңе’ҢйҖӮеәҰзҡ„еҠЁжҖҒи°ғж•ҙгҖӮдҫӢеҰӮпјҢе•Ҷеә—еҲ°й—Ёзҡ„иҙ§зү©дәӨд»ҳе’Ңе…¬и·Ҝиҙ§иҝҗйғҪжҳҜ常规жҙ»еҠЁпјҢдҪҶйңҖиҰҒиғҪеӨҹеңЁдёҖзі»еҲ—еҸҜиғҪжҖ§еҶ…еҜ№ж„ҸеӨ–жғ…еҶөеҒҡеҮәеҸҚеә”гҖӮеҗҢж ·пјҢеңЁз”ҹдә§зҺҜеўғдёӯпјҢжңәеҷЁдәәжү§иЎҢеӨ§йҮҸйҮҚеӨҚзҡ„еҠЁдҪңпјҢдҪҶеҝ…йЎ»е“Қеә”дёҚеҸҜйў„жөӢзҡ„еҸҳйҮҸпјҢдҫӢеҰӮе®ғжӯЈеңЁз»„иЈ…зҡ„组件зҡ„зІҫзЎ®ж–№еҗ‘пјҢжҲ–дҝ®ж”№д»»еҠЎд»Ҙе®ҡеҲ¶и®ўеҚ•гҖӮ
иҮӘдё»жңәеҷЁдәәзҡ„ж ёеҝғеҠҹиғҪжҳҜд»Җд№Ҳпјҹ
иҮӘдё»жңәеҷЁдәәзҡ„жҰӮеҝөеҫҲе№ҝжіӣпјҢеҸҜд»ҘеҢ…жӢ¬е…·жңүдёҚеҗҢеҠҹиғҪзҡ„еҗ„з§Қи®ҫеӨҮгҖӮдҪҶжҳҜпјҢд»»дҪ•иҮӘдё»жңәеҷЁдәәйғҪеә”иҜҘе…·еӨҮжү§иЎҢд»ҘдёӢеҹәжң¬еҠҹиғҪзҡ„иғҪеҠӣпјҡ
1. 收йӣҶе’ҢеӨ„зҗҶжңүе…ізҺҜеўғзҡ„дҝЎжҒҜгҖӮ
2. еңЁдёҚеҸҜйў„зҹҘзҡ„еҲәжҝҖдёӢй•ҝж—¶й—ҙе·ҘдҪңпјҢж— йңҖдәәдёәе№Ійў„гҖӮ
3. еңЁжІЎжңүдәәе·ҘеҚҸеҠ©зҡ„жғ…еҶөдёӢпјҲдҪҶжңүйў„е…ҲзЎ®е®ҡзҡ„йҷҗеҲ¶пјүеңЁе…¶ж“ҚдҪңзҺҜеўғдёӯ移еҠЁгҖӮ
4. йҒҝе…Қиў«зЁӢеәҸиҜҶеҲ«дёәдёҚеҸ—ж¬ўиҝҺзҡ„жғ…еҶөпјҢдҫӢеҰӮеҜ№дәәгҖҒиҙўдә§жҲ–иҮӘиә«зҡ„дјӨе®ігҖӮ
жӣҙе…Ҳиҝӣзҡ„жңәеҷЁдәәеҸҜиғҪиғҪеӨҹеңЁйҖҡиҝҮеӨ„зҗҶж•°жҚ®вҖңеӯҰд№ вҖқж—¶дјҳеҢ–е…¶ж•ҲзҺҮжҲ–ж·»еҠ ж–°еҠҹиғҪгҖӮжңәеҷЁдәәзҡ„иғҪеҠӣд№ҹеҸҜд»ҘйҖҡиҝҮйӣҶдҪ“ж•°жҚ®еӨ„зҗҶе®һзҺ°зҡ„зі»з»ҹеҚҮзә§жқҘжҸҗй«ҳгҖӮдҫӢеҰӮпјҢиҪҰйҳҹеҸҜд»ҘжҺҘ收е®ҡжңҹжӣҙж–°пјҢж №жҚ®еңЁдёҚеҗҢй©ҫ驶жқЎд»¶дёӢеҜ№е…¶йӣҶдҪ“иҝҗиҗҘж•°жҚ®зҡ„еӨ„зҗҶпјҢйҖҗжӯҘжҸҗй«ҳзҮғжІ№ж•ҲзҺҮгҖӮ
жЎҲдҫӢз ”з©¶.





