
Published on 01/20/2017 | Technology
MQTT is a machine-to-machine (M2M) and Internet of Things (IoT) open protocol standardized by the OASIS Technical Committee (www.oasis-open.org). The protocol is easy to adopt for a wide variety of IoT devices, platforms, and operating systems. Enterprise cloud platforms such as Microsoft Azure expose their IoT PaaS through MQTT.
This blog post covers the core concepts of MQTT that are necessary for building M2M and IoT applications. It covers the basic terminology, along with a section on integrating the MQTT with IoTView HMI.
MQTT was created in 1999 by Andy Stanford-Clark and Arlen Nipper. The motivation for designing MQTT was to create a lightweight and bandwidth-efficient protocol that was data agnostic with support for multiple levels of Quality of Service. Today, those are the same reasons for which MQTT is chosen for implementing IoT solutions.
How does MQTT Work?
MQTT was designed as an extremely lightweight Publish/Subscribe messaging transport. It is useful for connections with remote locations where a small code footprint is required and/or network bandwidth is at a premium.
MQTT uses the publisher & subscriber pattern to connect interested parties with each other. It does it by decoupling the sender-publisher with the receiver -subscriber. The publisher sends a message to a central topic which has multiple subscribers waiting to receive the message. The publishers and subscribers are autonomous, which means that they do not need to know the presence of each other.
Where can it be used?
The MQTT has been used in sensors communicating to a Broker via satellite link, over occasional dial-up connections, and in a range of automation and small device scenarios. It is also ideal for mobile applications because of its small size, low power usage, minimized data packets, and efficient distribution of information to one or many receivers
Terminology. What are Clients, Brokers. Topics?
Client – Any publisher or subscriber that connects to the centralized broker over a network is considered to be the client. It’s important to note that there are servers and clients in MQTT. Both publishers and subscribers are called as clients since they connect to the centralized service. Clients can be persistent or transient. Persistent clients maintain a session with the broker while transient clients are not tracked by the broker. Clients often connect to the broker through libraries (Sample libraries available for C, C++, Go, Java, C#, PHP, Python, Node.js, and Arduino) and software development toolkits (SDKs).
Broker: The Broker is primarily responsible for:
- receiving all messages and
- filtering them
- deciding who is interested
- sending the message to all subscribed clients
- the authentication and authorization of clients
It also holds the session of all persisted clients including subscriptions and missed messages.
The broker is the central hub, which every message needs to pass
Commercial MQTT brokers examples: HiveMQ,Xively, AWS IoT, Loop.
Topic:
A Topic In MQTT is a hierarchical structured string, which is used for message filtering and routing and determines which message gets to which client. It acts as the central distribution hub for publishing and subscribing messages.
Connection – MQTT can be utilized by clients based on TCP/IP. The standard port exposed by brokers is 1883, which is not a secure port. Those brokers who support TLS/SSL typically use port 8883. For secure communication, the clients and the broker rely on digital certificates.
Quality of Service
This value determines how the client and the server communicate to deliver the message.
Hands-on with MQTT
Now that the key concepts were covered, let’s see MQTT in action. This section will help you understand the essence of MQTT. IoT View Runtime of InTouch Machine Edition is used to illustrate. You can follow this link below to get your evaluation copy.
Installing the broker
One open source software MQTT broker is called Mosquitto. For installation instructions, please refer to the installation guide.
Architecture
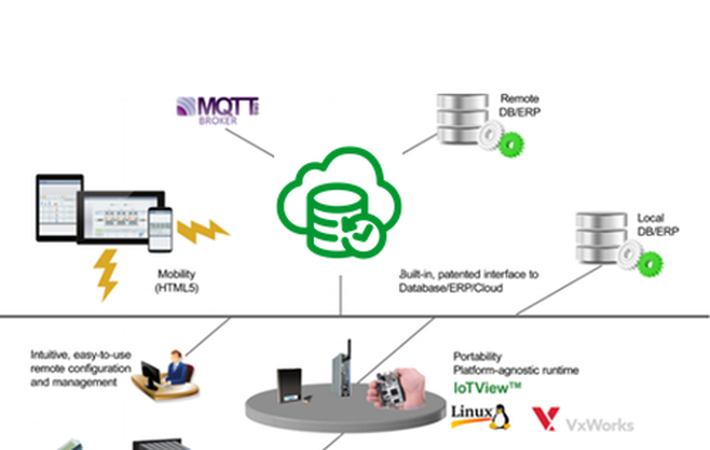
Sample Applications
- Distributed Data Acquisition, Manipulation and Control
- Centralized Management
Characteristics and Requirements
- Scalable – Large number of devices
- Secure – Encryption, Filtering, Remote notification
- Platform agnostic – Both local runtime and remote Thin Clients
- Simple – Easy to configure, deploy, and maintain
Wonderware Software value to customers:
CONNECT: Broadening the connectivity layer with low-cost, low-power sensors (Ex: IoTView)
COLLECT: Storing massive amounts of industrial data on premise and in the Cloud (Ex: Wonderware Online)
CONTEXTUALIZE: Converting industrial data to meaningful analytics (Ex: Prism)
CLOSE THE LOOP: Delivering real-time actionable information and business logic (Ex: Smart Glance)
InTouch Machine Edition is an easy to use development and runtime (ex: IoTView) software that is designed for the embedded operating systems. It has strong integration with the Wonderware portfolio of products such as System Platform and Wonderware Online. It is the perfect solution for embedded HMI on the plant floor, IIoT or IoT / Industry 4.0 solutions.
How is the InTouch Machine Edition & IoTView used?
Design an application once and deploy it to any embedded device that supports Windows Embedded, Linux and VxWork.
Remote visualization using web browsers or viewers
The MQTT driver build in the IoTView, is available for the following Runtime Target
Full RT – Windows PC Runtime
Embedded Standard – Runtime for Windows Embedded Standard
IoTView – Platform Agnostic Runtime (Linux)
Current MQTT Driver Limitations in IoTView
No support for Authentication
No support for SSL
For a free product download (it runs for 40 hours) click here: wonderware.com
MQTT seems to be the preferred protocol for M2M and IoT applications. Based on the publisher & subscriber pattern, it simplifies the connectivity between devices. This post attempted to introduce you to the basics of MQTT. I will cover other aspects of MQTT including cyber security and practical applications in the upcoming posts.
References:
This article was originally posted on Schneider Electric's blog.