Published on 12/26/2016 | Technology
Continuing my series of post on IoT/M2M and having been covered topics such as smart villages, communication protocols, role of telecom (part A and part B), managing road accidents, IoT for retail sector, smart home, smart clothes, IoT business models, best article aggregation and also what IoT really means to a layman - I think sensors deserve my attention - Here I will cover just basics of different type of sensors and their application.
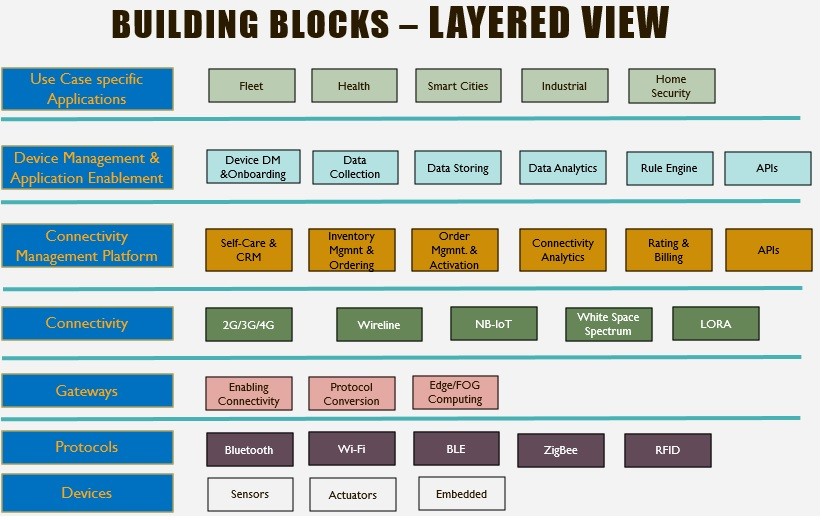
Before we move ahead lets take a look at the IoT technology stack in a layered view which shows that sensor and actuators forms the root of the IoT solution.
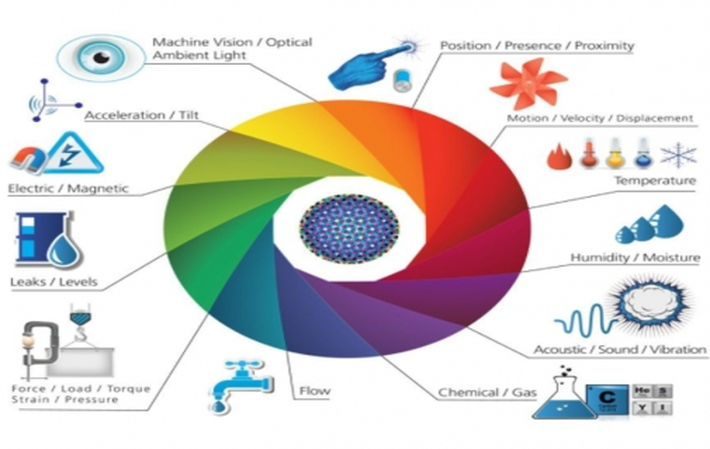
Now lets go through some widely used sensor types/categories.
Temperature/Heat
One of the most widely used sensor category which has application in energy mgmt, cars, manufacturing shop floor and environment. Here is Wikipedia list of sensors.
The LM35 series are precision integrated-circuit temperature devices with an output voltage linearly-proportional to the Centigrade temperature. The LM35 device has an advantage over linear temperature sensors calibrated in Kelvin, as the user is not required to subtract a large constant voltage from the output to obtain convenient Centigrade scaling. The LM35 device does not require any external calibration or trimming
The TMP36 is a low voltage, precision centigrade temperature sensor. It provides a voltage output that is linearly proportional to the Celsius temperature. It also doesn't require any external calibration to provide typical accuracies of ±1°C at +25°C and ±2°C over the −40°C to +125°C temperature range.
Temperature sensors are widely used in engineering and scientific applications, especially measurement systems. They are found within roadways in cold weather climates in order to help determine if icing conditions exist. Indoors, temperature sensors are used in several climate control systems including refrigerators, freezers, air conditioners and water heaters.
Humidity/Moisture
A humidity sensor (or hygrometer) senses, measures and reports the relative humidity in the air. It therefore measures both moisture and air temperature. Relative humidity is the ratio of actual moisture in the air to the highest amount of moisture that can be held at that air temperature. The warmer the air temperature is, the more moisture it can hold. There are many different kinds of humidity / dew sensors categorized by accuracy, operating temperature range, humidity range, supply voltage, packaging type and supply current. They find application in environment monitoring sector, supply chain, perishable food, agriculture/farming, health monitoring and also HVAC monitoring.
They can also be found in offices, cars, humidors, museums, industrial spaces and greenhouses and can be used in meteorology stations to report and predict weather. Dew sensors are used in the coating industry because the application of paint may be extremely sensitive to dew point. Future Electronics has done good job on listing the sensors and some definitions, I am reproducing some of them here.
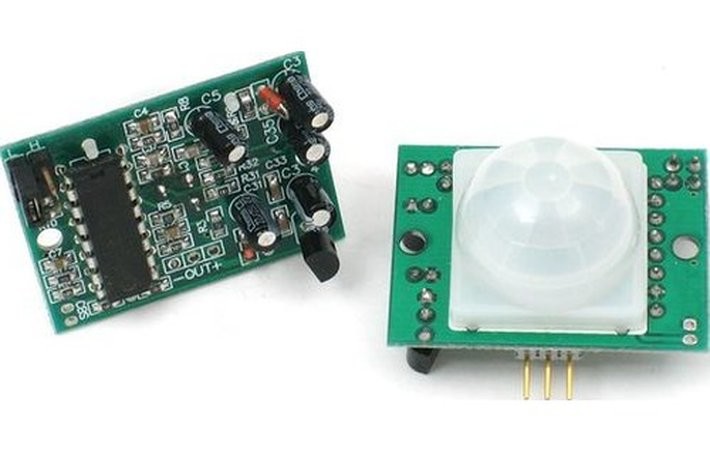

Accelerometers/Motion/Proximity
These type of sensors can be used to measure vehicle acceleration, vibration in vehicles, process control systems, machines, buildings and safety installations.
Motion (PIR) sensors are typically used in safety and security monitoring, detecting an intrusion, burglar alarm and kitchen garden protection. Gyro sensors are angular velocity sensing, angle sensing and control mechanisms to sense the vibrations produced by external factors.
Proximity sensors have a wide range of applications including parking assistance, conveyor systems, vibration measurements, roller coasters, anti-aircraft warfare, mobile phones and touch screens on mobile devices.
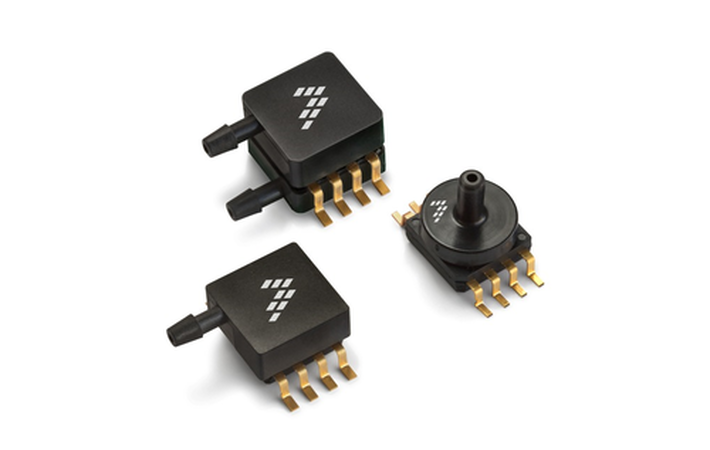

Pressure
Pressure sensors are very handy in different applications ranging from aircraft, automobiles, to weather instrumentation and any other machinery that has pressure functionality implemented. Other applications for pressure sensors include measuring flow and to calculate the level of a fluid or a loss of pressure due to a system leak. Example on the right -MPX5010/MPXV5010G/MP3V5010 series of piezoresistive transducers by NXP.
Position
Measurement applications for linear position sensors include coordinate-measuring machines, gear measurement tension testers, laser scanners and callipers, pick-and-place PCB assembly equipment, robotics, machine tools, wire bonders, printers and digital presses.
Angular position sensors can be found in a wide array of automotive applications including steering wheel, pedal, motor-shaft, throttle, torque, power seat and power mirror position sensing. They can also be used in industrial applications such as valve position sensing, in flow meters and in robotics.
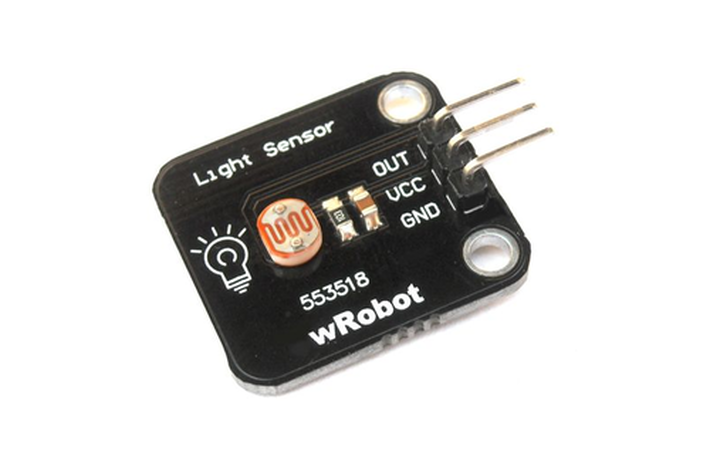

Light
A Light Sensor is something that a robot can use to detect the current ambient light level - i.e. how bright/dark it is. There are a range of different types of light sensors, including 'Photoresistors', 'Photodiodes', and 'Phototransistors'. Elprocus has described complete circuitry of light sensors here.
Light sensors have several uses in scientific applications. A light sensor may be part of a safety or security device like a garage door opener or a burglary alarm. Several modern electronics, including TV’s, computers and wireless phones use ambient light sensors in order to automatically control the brightness of a screen in situations where light intensity is high or low.
Magnetic
Magnetic field sensors, or "magnetometers", can be categorized into four general types depending on the magnitude of the measured field. If the targeted B-field is larger than the earth magnetic field (maximum value around 60 µT), the sensor does not need to be very sensitive. To measure the earth field larger than the geomagnetic noise(around 0.1 nT), better sensors are required.
For the application of magnetic anomaly detection, sensors at different locations have to be used to cancel the spatial-correlated noise in order to achieve a better spatial resolution. To measure the field below the geomagnetic noise, much more sensitive magnetic field sensors have to be employed. These sensors are mainly used in medical and biomedical applications, such as MRI and molecule tagging.
There are many approaches for magnetic sensing, including Hall effect sensor, magneto-diode, magneto-ransistor, AMR magnetometer, GMR magnetometer, magnetic tunnel junction magnetometer, magneto-optical sensor, Lorentz force based MEMS sensor, Electron Tunneling based MEMS sensor, MEMS compass, Nuclear precision magnetic field sensor, optically pumped magnetic field sensor, fluxgate magnetometer, search coil magnetic field sensor and SQUID magnetometer.
Image
Image sensors are simple, they can detect and convey the information that constitutes an image and plays a vital role on lot of security and safety applications. Read about what is CMOS here.
Other Categories
Hall Effect sensors are often seen in industrial applications and in consumer equipment. They can also be found in various types of sensors such as rotating speed sensors, current sensors, pressure sensors and fluid flow sensors.
More resources:
Postscapes: List of IoT sensors and actuators
INTEL: Sensor brings life to IOT
Mouser: Role of Sensors
Latest Sensor Articles
#sensors, #m2m, #iot, #actuators, #sensing
This article was originally posted on LinkedIn.